Kadena command-line reference
The Kadena command-line interface (kadena) provides direct access to the Kadena blockchain and to commands that help you create, deploy, and manage applications for the Kadena network.
You can use the Kadena command-line interface to perform tasks interactively or in scripts and automated workflows that don't allow interactive input.
The Kadena CLI has one primary entry point—the kadena parent command.
By providing a single entry point for performing a wide range of tasks, the Kadena CLI integrates naturally into the typical development workflow.
With commands designed specifically for building, testing, and managing Kadena-based applications, you can focus on building innovative applications using familiar tools.
Before you begin
What are the prerequisites? Node version? npm or pnpm version?
Install
The Kadena CLI is packaged in a TypeScript library that you can install using a package manager such as npm or pnpm.
For example, run the following command to install globally using npm:
npm install -g @kadena/kadena-clinpm install -g @kadena/kadena-cliRun the following command to install globally using pnpm:
pnpm install -g @kadena/kadena-clipnpm install -g @kadena/kadena-cliTo verify the package is installed and display usage information, type kadena and press Return:
kadenakadenaGet started
You can use the kadena parent command with different flags and subcommands to perform different types of operations.
The basic syntax for running kadena commands is:
kadena <subcommand> <action>kadena <subcommand> <action>Depending on the subcommand you select, the arguments, options, and flags you specify might apply to the parent command or to a specific subcommand. You can use the --help flag to display usage information for the kadena parent command, for a specified subcommand, or for a subcommand action.
For example, to see all of the options available for adding a new wallet, you can run the following command:
kadena wallet add --helpkadena wallet add --helpThe following diagram provides an overview of the kadena command-line interface:
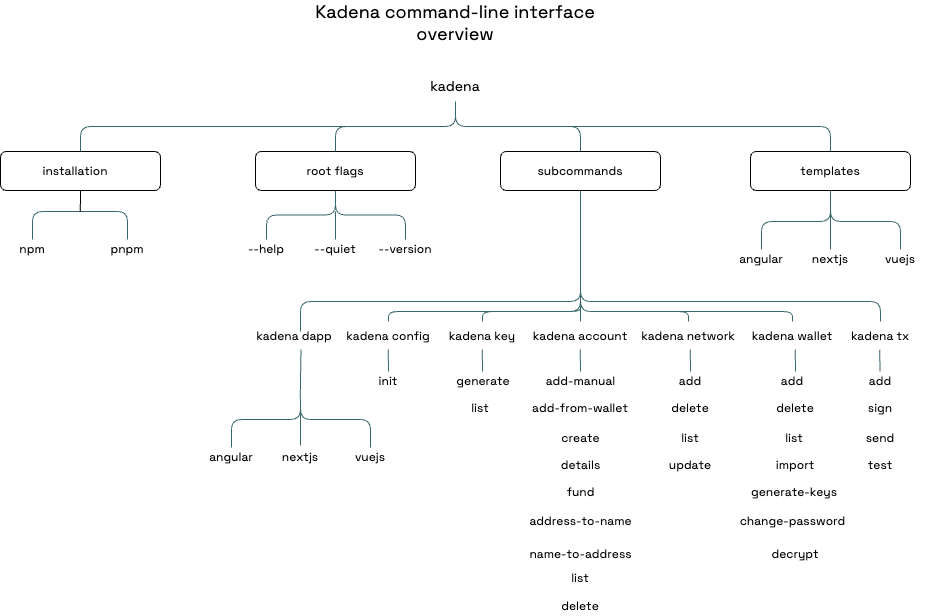
kadena
Use the kadena parent as the primary entry point for commands used to create, test, deploy, and managed decentralized applications you develop for the Kadena network.
Use the flags, subcommands, actions, and arguments to specify the operations you want to perform interactively or quiet mode.
Basic usage
The basic syntax for running kadena commands is:
kadena <subcommand> <action> [arguments] [flag]kadena <subcommand> <action> [arguments] [flag]Flags
You can use the following optional flags with the kadena parent command or with any of the kadena subcommands.
| Use this flag | To do this |
|---|---|
-h, --help | Display usage information. |
-q, --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations to enable automation of tasks. |
-V, --version | Display version information. |
Subcommands
Subcommands to perform actions or organized into categories that describe the subject of the action you want to perform.
For example, you can create and manage all wallet-related information using the wallet subcommand.
Use the following subcommands to select the category of information for the operation you want to perform.
| Use this subcommand | To do this |
|---|---|
config | Configure the initial context and properties for working with the kadena command-line interface. |
dapp | Create and manage an application project using a frontend framework template. |
wallet | Generate keys and manage wallets. |
key | Generate and manage public and secret keys. |
account | Create, fund, and manage accounts that contain fungibles assets. |
network | Create and manage network information. |
tx | Create and manage transactions. |
help | Display usage information for a specified command. |
version | Display version information. |
For reference information and examples, select an appropriate subcommand.
Interactive and quiet modes
If you want to minimize the information you enter on the command-line, you can enter arguments by responding to interactive prompts. Responding to prompts interactively is typically the best approach when getting started, eliminating the need to look up or remember the argument required for the action you want to perform. As you gain experience, you can reduce interactive prompting by specifying the arguments as part of the command.
If you want to disable all interactive prompts and confirmation messages, you can use the --quiet flag.
The --quiet flag enables you to automate tasks in environments where interactive input is impractical, such as continuous integration (CI) pipelines.
If you include the --quiet flag in a command, the command suppresses all interactive prompts and skips confirmations, so that the command executes uninterrupted.
This mode ensures that automated processes can run smoothly and efficiently, without the need for manual intervention.
Legacy mode
The --legacy flag ensures that the output format for commands related to wallets, keys, and transactions aligns with earlier cryptographic standards and with existing workflows and tools, such as Chainweaver.
This flag is especially useful if you need to interact with tools that rely on a legacy format for processing transactions or if you need to maintain backwards compatibility for a wallet or other application.
kadena config
Use kadena config to set up and manage the Kadena CLI environment.
Use kadena config init to create a .kadena folder with the default configuration for the development, test, and main Kadena networks.
Basic usage
The basic syntax for the kadena config command is:
kadena config <action> [flag]kadena config <action> [flag]Flags
You can use the following optional flags with the kadena config command.
| Use this flag | To do this |
|---|---|
-h, --help | Display usage information. |
-q, --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations to enable automation of tasks. |
-V, --version | Display version information. |
Actions
Use the following action to specify the operation you want to perform.
| Use this action | To do this |
|---|---|
init | Initialize the .kadena folder with default networks. |
Examples
To initialize your project with the default Kadena networks, run the following command:
kadena config initkadena config initThis command creates the .kadena folder in your current working directory and the devnets and networks subfolders with default settings for the network name, identifier, host, and block explorer for each network.
kadena dapp
Use kadena dapp to create a new decentralized application project from a frontend framework template.
Basic usage
The basic syntax for the kadena dapp command is:
kadena dapp <action> <argument> [flag]kadena dapp <action> <argument> [flag]Flags
You can use the following optional flags with the kadena dapp command.
| Use this flag | To do this |
|---|---|
-h, --help | Display usage information. |
-q, --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations to enable automation of tasks. |
-V, --version | Display version information. |
Actions
Use the following action to specify the operation you want to perform.
| Use this action | To do this |
|---|---|
add | Create a new project directory using a frontend framework template. |
help | Display usage information for a specified command. |
Arguments
The following table summarizes all of the options you can specify.
| Use this argument | To do this |
|---|---|
project-directory | Specify the name of the project directory. This argument is required. |
--dapp-template | Select the framework template to use for the new project. The valid framework templates are vuejs, nextjs, and angular. |
Examples
To create a new project using a Vue.js template, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena dapp add my-vuejs --dapp-template="vuejs"kadena dapp add my-vuejs --dapp-template="vuejs"If you are missing required dependencies for the template you select, you are prompted to install them. After running the command, you can change to your project directory by running a command similar to the following:
cd my-vuejscd my-vuejskadena key
Use kadena key to generate and manage public and secret keys.
Basic usage
The basic syntax for the kadena key command is:
kadena key <action> <argument> [flag]kadena key <action> <argument> [flag]Flags
You can use the following optional flags with the kadena keys command.
| Use this flag | To do this |
|---|---|
-h, --help | Display usage information. |
-l, --legacy | Generate keys using a legacy format. |
-q, --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations to enable automation of tasks. |
-V, --version | Display version information. |
Actions
Use the following action to specify the operation you want to perform.
| Use this action | To do this |
|---|---|
generate | Generate random public and secret key pairs. |
delete | Delete a public and secret key pair from the local filesystem. |
list | List all available keys. |
help | Display help for a specified command. |
Arguments
Depending on the action you select, you can specify different arguments and options.
The following table summarizes all of the options you can specify.
To see the options to use for a specific action, use the --help flag on the command-line or review the examples.
| Use this argument | To do this |
|---|---|
-a, --key-alias <keyAlias> | Set an alias for the key to store on the file system. |
-n, --key-amount <keyAmount> | Specify the number of key pairs to generate. The default is one. |
Examples
To generate a random public and secret key pair interactively, run the following command:
kadena keys generate --key-alias="myalias" --key-amount="2"kadena keys generate --key-alias="myalias" --key-amount="2"This command prompts you to enter the alias you want to use for the key and the number of keys to generate. After you respond to the prompts, the command displays confirmation that the keys were generated and where the key is stored on the local filesystem. For example:
Generated Plain Key Pair(s): Public Key Secret Key af042ef9<public-key> 52d872b1<secret-key> The Plain Key Pair is stored within your keys folder under the filename(s):Filenamepistolas.key Executed:kadena key generate --key-alias="pistolas" --key-amount="1" Generated Plain Key Pair(s): Public Key Secret Key af042ef9<public-key> 52d872b1<secret-key> The Plain Key Pair is stored within your keys folder under the filename(s):Filenamepistolas.key Executed:kadena key generate --key-alias="pistolas" --key-amount="1" To generate two public and secret key pairs, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena key generate --key-alias="myalias" --key-amount="2"kadena key generate --key-alias="myalias" --key-amount="2"To generate a public and secret key pair using a legacy format for backward compatibility, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena key generate --key-alias="myalias" --key-amount="5" --legacykadena key generate --key-alias="myalias" --key-amount="5" --legacyTo list information about available keys, you can run the following command:
kadena keys listkadena keys listThis command displays information similar to the following:
Alias Index Legacy Public Key Secret Key myalias-1.key 1 No 8724e659<public-key> 5a2410de<secret-key>myalias.key 0 No 6ab6cffe<public-key> 45b829ee<secret-key>pistolas.key 0 No dd4a1a4a<public-key> 2c1863f3<secret-key>Alias Index Legacy Public Key Secret Key myalias-1.key 1 No 8724e659<public-key> 5a2410de<secret-key>myalias.key 0 No 6ab6cffe<public-key> 45b829ee<secret-key>pistolas.key 0 No dd4a1a4a<public-key> 2c1863f3<secret-key>To delete a key interactively, you can run the following command:
kadena key deletekadena key deleteThis command prompts you to select all key files or a specific key file. After you select the key file you want to delete, you are prompted to confirm the selection. For example:
? Select a key file: test.key: af042....5b9b9f? Are you sure you want to delete the key: "test.key"? Yes the key: "test.key" has been deleted Executed:kadena key delete --key-files="test.key" --confirm ? Select a key file: test.key: af042....5b9b9f? Are you sure you want to delete the key: "test.key"? Yes the key: "test.key" has been deleted Executed:kadena key delete --key-files="test.key" --confirm kadena network
Use kadena network to add and manage Kadena networks and network information.
Basic usage
The basic syntax for the kadena network command is:
kadena network <action> <arguments> [flag]kadena network <action> <arguments> [flag]Flags
You can use the following optional flags with the kadena network command.
| Use this flag | To do this |
|---|---|
-h, --help | Display usage information. |
-q, --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations to enable automation of tasks. |
-V, --version | Display version information. |
Actions
Use the following actions to specify the operation you want to perform.
| Use this action | To do this |
|---|---|
add | Add a new local network configuration. |
list | List all available local networks. |
update | Update existing network information. |
delete | Delete an existing network configuration. |
help | Display help for a specified command. |
Arguments
Depending on the action you select, you can specify different arguments and options.
The following table summarizes all of the arguments you can specify.
To see usage information for a specific action, use the --help flag in the command-line or see the examples for performing specific tasks.
| Use this argument | To do this |
|---|---|
-n, --network-name <networkName> | Specify the name of the network to act on. |
--network-id <networkId> | Specify the identifier for the network to act on. |
--network-host <networkHost> | Specify the host for the network to act on. |
--network-explorer-url <networkExplorerURL> | Specify the explorer URL for the network to act on. |
--network-overwrite yes | no |
--network-delete yes | no |
Examples
To add a new network configuration, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena network add \ --network-name="mydevnet" \ --network-id="mydevnet01" \ --network-host="localhost:8081" \ --network-explorer-url="https://explorer.localhost:8081" \ --network-overwrite="yes"kadena network add \ --network-name="mydevnet" \ --network-id="mydevnet01" \ --network-host="localhost:8081" \ --network-explorer-url="https://explorer.localhost:8081" \ --network-overwrite="yes"If you leave out any of the arguments, you are prompted interactively to provide the missing information. Because this example specifies all of the arguments, the command creates the network and displays output similar to the following:
The network configuration "mydevnet" has been saved.The network configuration "mydevnet" has been saved.To list the details for all networks, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena network listkadena network listThis command displays information similar to the following:
Network Network ID Network Host Network Explorer URL mydevnet mydevnet01 localhost:8081 https://explorer.localhost:8081Network Network ID Network Host Network Explorer URL mydevnet mydevnet01 localhost:8081 https://explorer.localhost:8081To update the information for a network, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena networks update \ --network-name="mydevnet" \ --network-id="mydevnet01" \ --network-host="https://api.chainweb.com" \ --network-explorer-url="https://explorer.chainweb.com/mainnet/tx/"kadena networks update \ --network-name="mydevnet" \ --network-id="mydevnet01" \ --network-host="https://api.chainweb.com" \ --network-explorer-url="https://explorer.chainweb.com/mainnet/tx/"To delete an existing network, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena network delete \ --network="mydevnet" \ --network-delete="yes"kadena network delete \ --network="mydevnet" \ --network-delete="yes"kadena account
Use kadena account to add, fund, and manage Kadena accounts and fungible assets.
Basic usage
The basic syntax for the kadena account command is:
kadena account <action> <arguments> [flag]kadena account <action> <arguments> [flag]Flags
You can use the following optional flags with the kadena account command.
| Use this flag | To do this |
|---|---|
-h, --help | Display usage information. |
-q, --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations to enable automation of tasks. |
-V, --version | Display version information. |
Actions
Use the following actions to specify the operation you want to perform.
| Use this action | To do this |
|---|---|
| create [options] | Create an account on the Kadena public blockchain network (mainnet). |
| add-manual [options] | Add an existing account locally to the CLI. |
| add-from-wallet [options] | Add a local account from a key wallet. |
| delete [options] | Delete a local account. |
| details [options] | Get details for a specified account. |
| fund [options] | Fund a specified new or existing account. |
| list [options] | List all available accounts. |
| name-to-address [options] | Resolve a .kda name to a k:account The k: prefix refers to Kadena account name associated with a public key. |
| address-to-name [options] Resolve a k:account to a .kda name. | |
| help [command] | Display help for a specified command. |
Arguments
Depending on the action you select, you can specify different arguments and options.
The following table summarizes all of the arguments you can specify.
To see usage information for a specific action, use the --help flag in the command-line or see the examples for performing specific tasks.
| Use this argument | To do this |
|---|---|
--account-alias <accountAlias> | Specify an alias to store your account information. |
-a, --account-name <accountName> | Specify the account name associated with one or more specified public keys. |
-f, --fungible <fungible> | Specify the name of a fungible asset type. The valid values are coin and nft. The default is coin. |
-n, --network <network> | Specify the Kadena network name—for example, testnet or mainnet—to use. |
-c, --chain-id <chainId> | Specify the chain identifier to use. |
-p, --public-keys <publicKeys> | Specify public keys for an account in a comma-separated list. |
-p, --predicate <predicate> | Specify the number of signatures required in a keyset for a transaction to be valid. You can specify keys-all, keys-any, keys-2, or a custom predicate. |
-w, --wallet-name <walletName> | Specify the wallet name you are adding an account from. |
-o, --account-overwrite | Overwrite account details from the chain. |
-a, --account-kdn-name <accountName> | Specify the Kadena domain address (.kda) that you want to translate to a Kadena account name. |
-a, --account-kdn-address <accountKdnAddress> | Specify the Kadena account name (k: prefix) that you want to translate to a Kadena domain address (.kda). |
-c, --confirm | Confirm that you want to delete a specified account. |
-h, --help | Display help for a specified command. |
Examples
To create an account on the Kadena public blockchain network (mainnet) interactively, run the following command:
kadena account createkadena account createTo add an account on the development network manually, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena account add-manual --account-alias="pistolas" --account-name="k:bbccc99ec-accountname" --fungible="coin" --network="devnet" --chain-id="1" --public-keys="bbccc99ec-publickey" --predicate="keys-all"kadena account add-manual --account-alias="pistolas" --account-name="k:bbccc99ec-accountname" --fungible="coin" --network="devnet" --chain-id="1" --public-keys="bbccc99ec-publickey" --predicate="keys-all"To add an account on the test network from a wallet you've exported to a file, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena account add-from-wallet --account-alias="myalias" --wallet="mywallet.wallet" --fungible="coin" --network="testnet" --chain-id="5" --public-keys="publickey" --predicate="keys-all"kadena account add-from-wallet --account-alias="myalias" --wallet="mywallet.wallet" --fungible="coin" --network="testnet" --chain-id="5" --public-keys="publickey" --predicate="keys-all"To see details about an account by using the account alias, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena account details --account="pistolas" --network="testnet" --chain-id="1" kadena account details --account="pistolas" --network="testnet" --chain-id="1" This command returns output similar to the following for the specified alias:
Details of account "pistolas" on network "testnet04" and chain "1" is: Account Name Public Keys Predicate Balance k:5ec41b89....bc76dc5c35e2c0 5ec41b89....c35e2c0 keys-all 69.9986947922 Executed:kadena account details --account="pistolas" --network="mainnet" --chain-id="1"Details of account "pistolas" on network "testnet04" and chain "1" is: Account Name Public Keys Predicate Balance k:5ec41b89....bc76dc5c35e2c0 5ec41b89....c35e2c0 keys-all 69.9986947922 Executed:kadena account details --account="pistolas" --network="mainnet" --chain-id="1"To fund an account on the test network using the account alias, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena account fund --account="pistolas" --amount="10" --network="testnet" --chain-id="2"kadena account fund --account="pistolas" --amount="10" --network="testnet" --chain-id="2"To display the Kadena account name (k: prefix) for a specified Kadena domain address (.kda) name, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena account name-to-address --network="mainnet" --account-kdn-name="kadena.kda"kadena account name-to-address --network="mainnet" --account-kdn-name="kadena.kda"To display the Kadena domain address (.kda) for a specified Kadena account name (k: prefix) name, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena account address-to-name --network="mainnet" --account-kdn-address="k:3b60fe83bc63cc9c797cf13d153b5f90dc538be97246a79561fe488490112886"kadena account address-to-name --network="mainnet" --account-kdn-address="k:3b60fe83bc63cc9c797cf13d153b5f90dc538be97246a79561fe488490112886"To list account information for a specified account alias, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena account list --account-alias="pistolas"kadena account list --account-alias="pistolas"This command returns output similar to the following for the specified alias:
Account Alias Account Name Public Key(s) Predicate Fungiblepistolas k:5ec41b89d323....bc76dc5c35e2c0 5ec41b89d3....dc5c35e2c0 keys-all coin Account Alias Account Name Public Key(s) Predicate Fungiblepistolas k:5ec41b89d323....bc76dc5c35e2c0 5ec41b89d3....dc5c35e2c0 keys-all coin To list account information for all account aliases, you can specify --account-alias="all" in the command.
To delete a specific account:
kadena account delete --account-alias="nft-owner" --confirm
To delete all accounts:
kadena account delete --account-alias="all" --confirm
kadena tx
Use kadena tx to create, submit, and manage transactions.
Basic usage
The basic syntax for the kadena tx command is:
kadena tx <action> <arguments> [flag]kadena tx <action> <arguments> [flag]Flags
You can use the following optional flags with the kadena tx command.
| Use this flag | To do this |
|---|---|
-h, --help | Display usage information. |
-l, --legacy | Sign transaction using a legacy format. |
-q, --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations to enable automation of tasks. |
-V, --version | Display version information. |
Actions
Use the following actions to specify the operation you want to perform.
| Use this action | To do this |
|---|---|
| send [options] | Send a transaction to the network. |
| sign [options] | Sign a transaction using your local wallet/aliased file/keypair. |
| test [options] | Test a signed transaction on testnet. |
| add [options] | Select a template and add a transaction. |
| list [options] | List transactions. |
| help [command] | Display usage information for a specified command. |
Arguments
Depending on the action you select, you can specify different arguments and options.
The following table summarizes all of the options you can specify.
To see the options to use for a specific action, use the --help flag on the command-line or review the examples.
| Use this argument | To do this |
|---|---|
--directory <directory> | Specify the directory that contains the transaction file. The default is your current working directory. |
-s, --tx-signed-transaction-files <txSignedTransactionFiles> | Specify the name of signed transaction files. You can specify multiple files in a comma-separated list. |
-n, --tx-transaction-network <txTransactionNetwork> | Specify the Kadena networks that you want to send the transaction to. You can specify networks in a comma-separated list in the order you want the transaction sent. For example, to send a transaction to the development network then the test network, you can specify "devnet, testnet" |
-p, --poll | Poll for transaction status. |
-s, --tx-sign-with <txSignWith> | Select a signing method for a transaction. The valid signing methods are keyPair, aliasFile, and localWallet. |
-w, --wallet-name <walletName> | Specify the wallet to use to sign a transaction. |
--password-file <passwordFile> | Specify the path to the password file. |
-u, --tx-unsigned-transaction-files <txUnsignedTransactionFiles> | Specify the name of unsigned transaction files that you want to sign using the specified signing method. You can specify multiple files in a comma-separated list. |
-a, --key-alias-select <keyAliasSelect> | Sign a transaction using the specified key alias. |
-k, --key-pairs <keyPairs> | Specify key pairs as strings on the command-line. You can specify multiple key pairs separated by semi-colons (;). |
-n, --network <network> | Specify the Kadena network name—for example, testnet or mainnet—to use. |
-c, --chain-id <chainId> | Specify the chain identifier to use. |
--template <template> | Select a template for adding a transaction. |
--template-data <templateData> | Specify a template data file for adding a transaction. |
--template-variables <templateVariables> | Specify template variables to use for adding a transaction. |
-o, --out-file <outFile> | Specify the file name to save the output from adding a transaction. |
Examples
To sign an unsigned transaction using a public and secret key pair, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena tx sign --tx-sign-with="keyPair" --key-pairs="publicKey=xxx,secretKey=xxx" --tx-unsigned-transaction-files="transaction-(request-key).json"kadena tx sign --tx-sign-with="keyPair" --key-pairs="publicKey=xxx,secretKey=xxx" --tx-unsigned-transaction-files="transaction-(request-key).json"To sign two unsigned transactions using a key alias file from a wallet, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena sign --tx-sign-with="aliasFile" --wallet-name="mywallet.wallet" --key-alias-select="mywalletalias.key" --tx-unsigned-transaction-files="transaction-(request-key).json,transaction-(request-key).json"kadena sign --tx-sign-with="aliasFile" --wallet-name="mywallet.wallet" --key-alias-select="mywalletalias.key" --tx-unsigned-transaction-files="transaction-(request-key).json,transaction-(request-key).json"You can use the kadena tx test command to use a local API endpoint to check whether a signed transaction for a specified network is viable without submitting the transaction.
By using the local endpoints, you can dry-run smart contract code using data in the coin contract tables without paying transaction fees.
To test whether a signed transaction would be successful on the test network using the local endpoint, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena tx test --network="testnet" --directory="./my-tx" --tx-signed-transaction-files="transaction-(request-key)-signed.json" --chain-id="1"kadena tx test --network="testnet" --directory="./my-tx" --tx-signed-transaction-files="transaction-(request-key)-signed.json" --chain-id="1"To send a signed transaction to the Kadena main network and test network, you can run a command similar to the following:
kadena tx send --tx-signed-transaction-files="transaction-I4WaMUwQZDxhaf2r2FZj0TQf7Zv1J5v45Yc2MYxPURU-signed.json" --tx-transaction-network "mainnet, testnet" --pollkadena tx send --tx-signed-transaction-files="transaction-I4WaMUwQZDxhaf2r2FZj0TQf7Zv1J5v45Yc2MYxPURU-signed.json" --tx-transaction-network "mainnet, testnet" --pollThe kadena tx add command enables you to create transactions using templates in combination with values you specify to generate the most common types of transactions that are ready to sign and submit across multiple chains with minimal effort.
Currently, there are two default templates—transfer and safe-transfer—to enable to you create transactions that transfer tokens between accounts.
For more information about using templates to generate transactions, see Code templates.
To generate a transaction from a template interactively, you can run the following command:
kadena tx addkadena tx addThis command then prompts you to select the template to use and information about the account to transfer from and the account to transfer to. enter the alias you want to use for the key and the number of keys to generate.
For example:
? Which template do you want to use: transfer.ktpl? File path of data to use for template .json or .yaml (optional):? Template value account-from:k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e? Template value account-to:k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e? Template value decimal-amount: 1.0? Template value chain-id: 1? Template value pk-from:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e? Template value network-id: testnet? Where do you want to save the output: my-test-output? Which template do you want to use: transfer.ktpl? File path of data to use for template .json or .yaml (optional):? Template value account-from:k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e? Template value account-to:k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e? Template value decimal-amount: 1.0? Template value chain-id: 1? Template value pk-from:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e? Template value network-id: testnet? Where do you want to save the output: my-test-outputAfter you respond to the prompts, the command displays the transaction you constructed and confirms the location of the file containing the unsigned transaction.
kadena wallet
Usage: index wallet [options] [command]
Tool to generate and manage wallets
Options: -h, --help display help for command
Commands: add [options] Add a new local wallet import [options] Import (restore) wallet from mnemonic phrase generate-keys [options] Generate public/secret key pair(s) from your wallet change-password [options] Update the password for your wallet decrypt [options] Decrypt message delete [options] Delete wallet from your local filesystem list [options] List wallet(s) help [command] display help for command