Set up a local development network
The first step in developing smart contracts using Pact is to set up a local development environment. If you followed the steps in Deploy your first contract, you should already have a local development network running in a Docker container.
Your local development environment should also include:
- An internet connection and a web browser installed on your local computer.
- An integrated development environment (IDE) or code editor such as Visual Studio Code.
- Access to an interactive terminal shell as part of the IDE or code editor you use.
Start the development network
If you haven't downloaded the Docker image for the development network or have stopped the container, you should pull the latest image and start the network on your local computer. The development network includes several commonly-used contracts deployed by default. These contracts provide functions you can reuse to perform common tasks like creating accounts and transferring funds.
To start the local development network:
-
Open a terminal shell on your computer.
-
Start the Docker service if it isn't configured to start automatically.
-
Start the container without a persistent volume by running the following command:
docker run --interactive --tty --publish 8080:8080 kadena/devnet:latestdocker run --interactive --tty --publish 8080:8080 kadena/devnet:latestYou can stop the network at any time—and reset the blockchain state—by pressing Ctrl-c in the terminal.
Install Pact
You can run Pact in a browser or install it locally on your local computer. In most cases, you should install Pact locally as part of your private development environment. Depending on your operating system platform and preferred tools, you can download and install Pact prebuilt binaries or build Pact from its source code.
Install from binaries
You can download and install Pact binaries for Linux or macOS computers from Pact Releases.
Use Homebrew
On macOS, you can install Pact using Homebrew byt running the following commands:
brew updatebrew install kadena-io/pact/pactbrew updatebrew install kadena-io/pact/pactBuild from source
To build Pact binaries directly from source, download the source code from Pact Releases, then use Homebrew, Cabal, or Nix to build Pact. For more information about the dependencies and tools for building from the source code, see Building from source.
Install the language server
You can install the Pact language server plugin on your local computer to support syntax highlighting and other features in the code editor.
Configure Visual Studio Code
If you use Visual Studio Code as your integrated development environment (IDE), you can install the Pact extension to streamline your smart contract development experience. Before installing the extension, verify that you have Pact and the Pact Language Server installed.
Install the Pact extension
To install the Pact extension:
-
Open Visual Studio Code.
-
Select View, then click Extensions.
-
Type pact in the Search field.
-
Select PactLang, then click Install.
If you're prompted to install additional extensions, you should install them to enable the full functionality of the Pact extension.
Configure Pact settings
To configure the Pact extension settings:
-
Select Code, Settings, then click Settings and search for pact.
-
Select Pact configuration and configure the settings appropriate for your development environment.
-
Select Enable coverage to enable code coverage reporting for
.pactand.replfiles.With this option enabled, code coverage is calculated for the
.replfile and all of the.pactand.replfiles that it loads every time you save a.replfile.Covered lines aree highlighted in green in your editor and uncovered lines aree highlighted in red. To view a code coverage report in HTML format, right-click the
./coverage/html/index.htmlfile relative to the file that was run. Click Show preview to open the report.To run code coverage for all your
.replfiles at once, create an entry point.replfile that loads all the other.replfiles in your project. You can then open the entry point file and save it to run all of your tests. -
Select Enable Lsp to enable the Pact Language server.
With this option enabled, syntax errors are be highlighted in
.pactfiles and problems are reported in the Visual Studio Code status bar and bottom panel. -
Select Enable trace to enable the output trace for Pact.
With this option enabled, the
pactcommand runs with the--traceoption every time you save a file. The--traceoption provides detailed line by line information about.pactand.replfile execution. -
Set the path to the Pact executable and the Pact Language server executable.
If you added the executables to your
PATH, you can usepactandpact-lspfor these settings.
Configure Pact settings
Install Chainweaver
Chainweaver integrates the management of wallets, accounts, and keys with signing and editing features that you can use as you develop smart contracts using the Pact programming language. With Chainweaver, you can build, test, and iterate on your smart contracts before deploying them to your local development network, the Kadena test network, or the Kadena main network.
Chainweaver includes a built-in read-eval-print-loop (REPL) interactive interpreter that enables you to write and execute Pact code in the desktop or web-based application. You can also use Chainweaver to:
- Explore smart contract modules and functions.
- Define and manage authorization rules in keysets.
- Deploy smart contracts on a network.
- Update previously-deployed contracts.
If you don't already have a Chainweaver account, you should create one using either the Chainweaver desktop application or the Chainweaver web application. After you download and install the desktop application or open Chainweaver in a browser, you can create a wallet and accounts to interact with Kadena networks.
When you open and unlock Chainweaver, the navigation panel on the left is collapsed to only display icons by default. The navigation panel provides access to the tools for managing your accounts, keys, and development environment.
| Icon | Section | What you can do here |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts | View and manage your accounts, add account names to your watch list, transfer funds between accounts and across chains, and view transaction status. | |
| Keys | Generate, view, and manage public keys associated with your secret key. | |
| Signature Builder | Construct the signatures needed to sign transactions. | |
| Contracts | Access a code editor and development tools for writing, testing, and deploying Pact modules and smart contracts. | |
| Resources | Explore documentation and Chainweaver resources. | |
| Settings | Configure your network and account settings. | |
| Log out | Log out of the current session. |
Connect to the development network
By default, Chainweaver lets you connect to the Kadena test network and the Kadena main network. However, as you start writing Pact modules, you'll want to test and deploy them on your local development network. Before you can do that, you need to configure Chainweaver to connect to the local host and port number running the development network.
To connect to the development network:
-
Click Settings in the Chainweaver navigation panel.
-
Click Network.
-
In Edit Networks, type a network name, then click Create.
-
Expand the new network, then add the localhost as a node for this network by typing
127.0.0.1:8080.If the local computer is still running the development network Docker container, you should see the dot next to the node turn green.
-
Click Ok to close the network settings.
Navigate smart contracts
After you connect Chainweaver to the development network, you can use Chainweaver to deploy and manage the smart contracts you develop. You can access the Chainweaver development environment by clicking Contracts in the navigation panel.
After you click Contracts, Chainweaver displays common tasks and two working areas:
- The left side displays a sample contract in a code editor that you can use to view and edit contract code.
- The right side provides controls that enable you to navigate between contracts, view contract details, manage keys, and test operations for contracts you have deployed.
The common tasks enable you to:
- Browse to an open a file from the file system.
- Load your contract into the Pact interactive REPL where you can run Pact commands.
- Deploy the selected contract on the active blockchain network.
You'll use Load into REPL and Deploy frequently as you start writing Pact modules and deploy modules on the local development network.
Code editor
Within the Contracts development environment, the code editor enables you to view and modify contract code using a familiar editing interface. It's similar to other code editors with support for copying and pasting text, syntax highlighting, and inline error reporting.
You can hover the cursor over lines that indicate errors to view information about the problem to help you determine how to fix it.

The Chainweaver code editor also supports formal verification. Formal verification is a process that enables you to automatically test the correctness of your code for potential errors and security vulnerabilities. With this process, you can mathematically prove that your contract has no security vulnerabilities, ensuring you can create secure code quickly and effectively.
For more information about how formal verification helps you develop safer smart contracts, see Pact Formal Verification: Making Blockchain Smart Contracts Safer.
Contract navigation and developer tools
The right side of the Contracts development environment provides many useful features and tools for developing smart contracts. For example, there are features to help you set up your environment, run commands in the interactive REPL, read messages, and explore other modules that exist on the network.
Env
Select Env to view and fix errors or manage authorization data in keysets. If the error and warning detected can be fixed automatically, you'll see the Fix option.
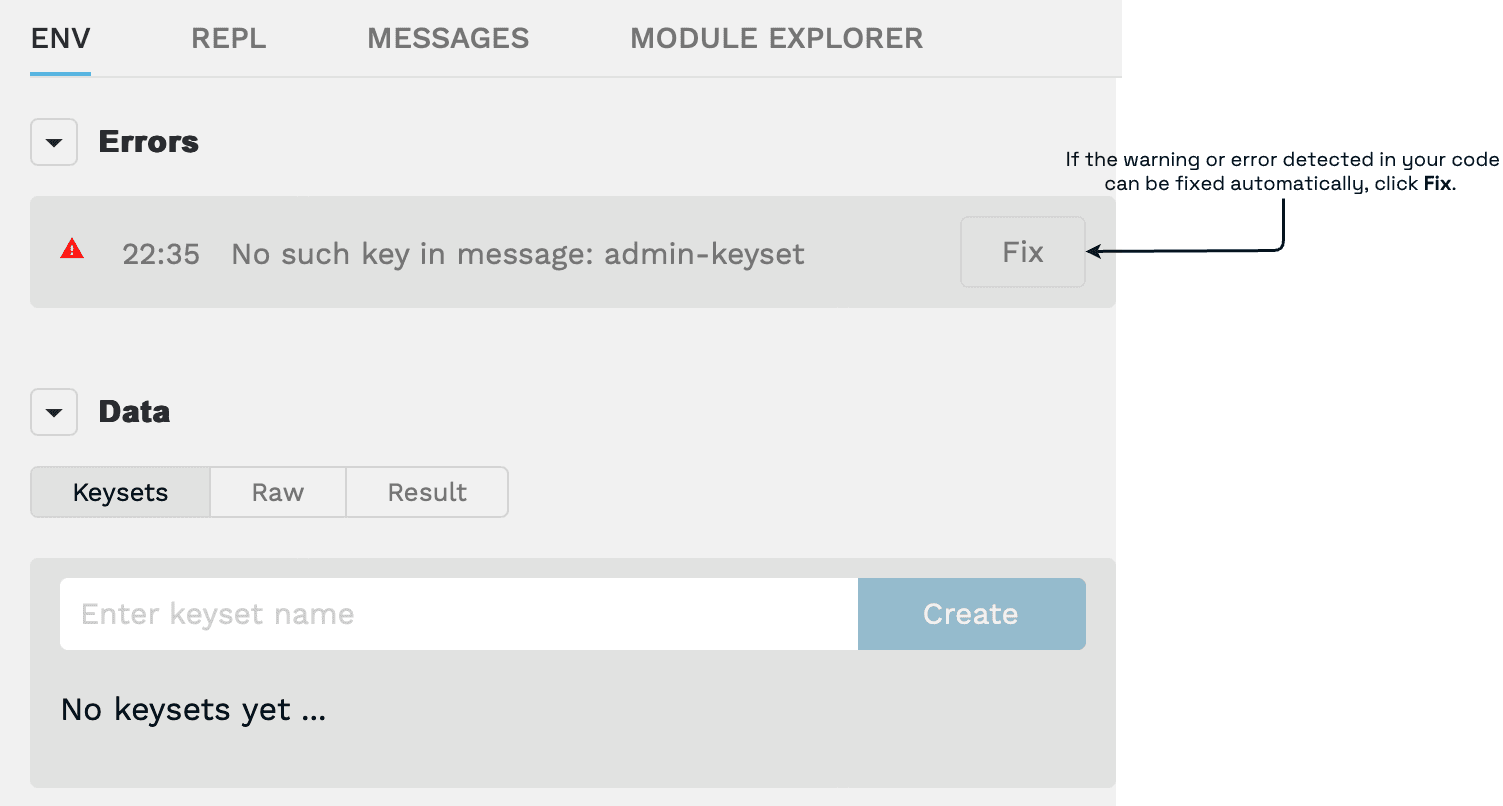
In this example, the error is a missing keyset and you can click Fix to automatically create the keyset and add it to the Data section.
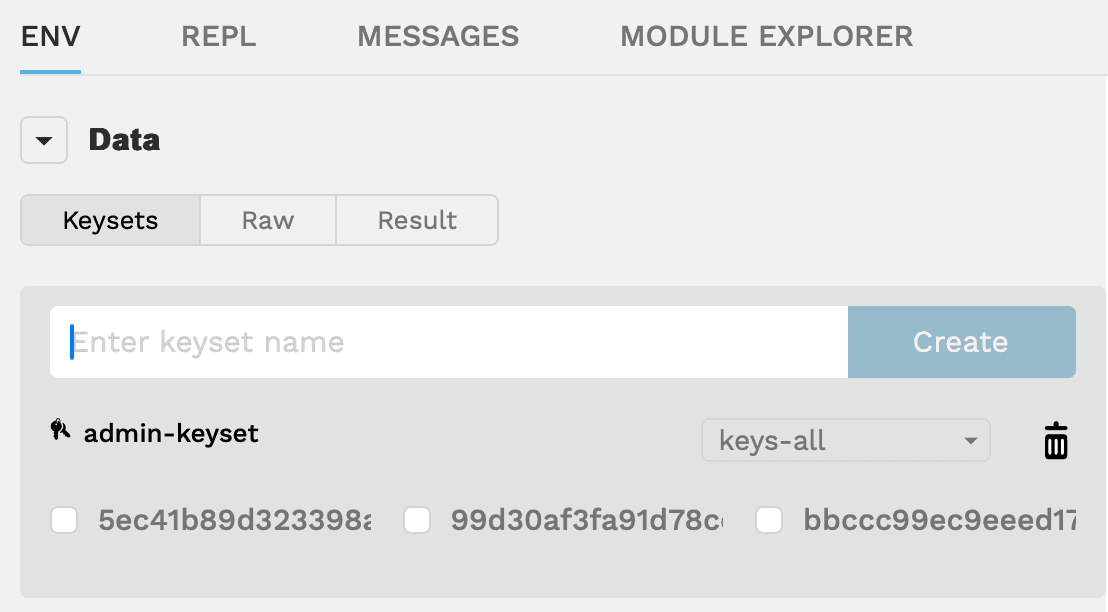
If you delete the keyset created for you, you can use the Data section to create a keyset by typing a keyset name, then clicking Create. By default, keysets require all of the keys associated with an account to sign transactions, so you'll see keys-all selected for the new keyset. You'll learn more about keysets, in Keysets.
You can also create keysets manually using the JSON format by clicking Raw, then defining the keyset name, keys, and pred values. You can see the JSON format for keysets you have created by clicking Result.
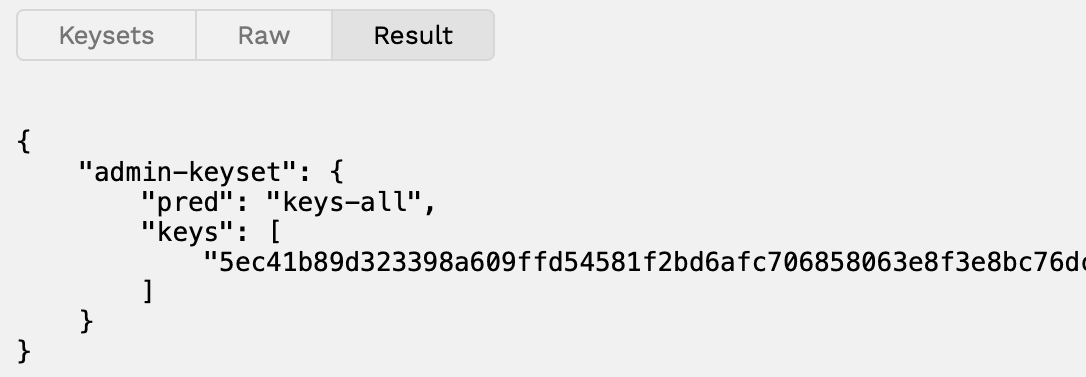
The pred field specifies a predicate function to use for the keyset.
The predicate function returns a boolean value evaluating to true or false.
In this case, the predicate option evaluated is keys-all and it returns true if all of the keys listed in the keyset—in this example, only one key—sign the transaction.
REPL
A great way to get started with Pact is by writing some simple code for yourself. The REPL enables you to run Pact commands directly in the browser. Select REPL to open the Pact interactive interpreter, then try running the following commands to start learning Pact syntax conventions.
Numbers
Pact uses prefix notation for math operators. With prefix notation, the operator precedes the values it’s operating on. For example, you can add two numbers with the following command:
(+ 2 2)4(+ 2 2)4To subtract two numbers:
pact>(- 4 9)-5pact>(- 4 9)-5To multiply two numbers:
pact>(* 3 4)12pact>(* 3 4)12Strings
You can concatenate strings using a plus (+) as a prefix. For example, you can concatenate the strings "Hello" and "REPL" with the following command:
pact > (+ "Hello" " REPL")“Hello REPL”pact > (+ "Hello" " REPL")“Hello REPL”Lists
You can specify lists using square brackets ([ ]) with or without commas.
For example, you can specify the elements in a list without using commas:
pact> [1 2 3][1 2 3]pact> [1 2 3][1 2 3]To specify the elements in a list using commas:
pact>["blue","yellow","green"]["blue" "yellow" "green"]pact>["blue","yellow","green"]["blue" "yellow" "green"]Objects
You can create objects using curly braces ({ }) with key-value pairs separated by a colon (:).
For example:
pact> { "foo": (+ 1 2), "bar": "baz" }{ "foo": 3, "bar": "baz" }pact> { "foo": (+ 1 2), "bar": "baz" }{ "foo": 3, "bar": "baz" }You can view more commands to try in Syntax and keywords and Pact functions.
Run commands in the code editor
You can also run commands in the code editor. To run commands in the code editor, delete existing code from the code editor type a command, then click Load into REPL.
Messages
Code editors often provide messages to help you identify errors and log outputs. These messages are useful for debugging programs and fixing potential issues with your contract. Select Messages to view messages from the code editor in Chainweaver.
Module Explorer
Select Module Explorer to open and view sample smart contracts, search for and view deployed contracts, and call functions from any contract that exists on the active network.
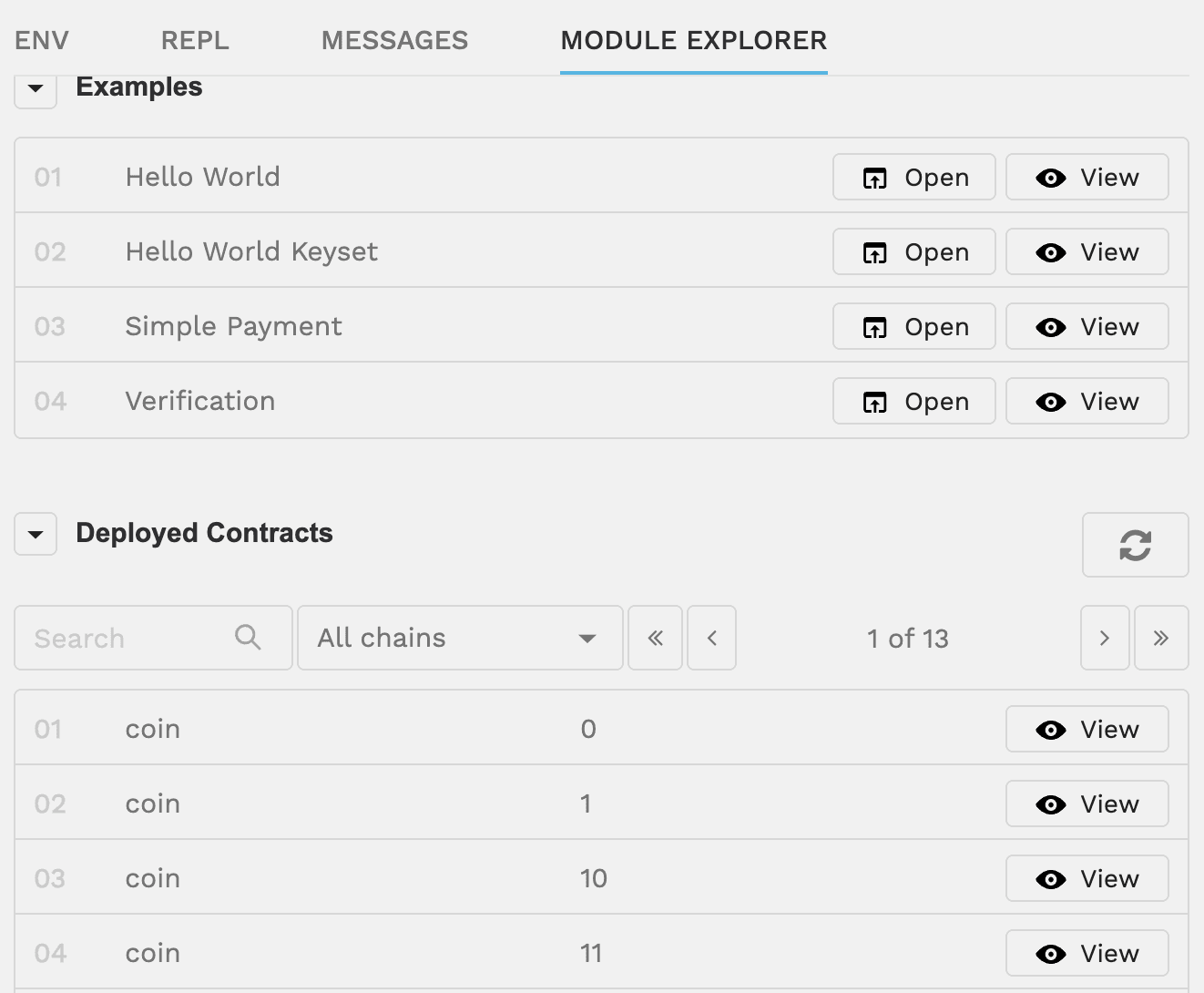
Under Examples, you can click Open next to an example contract name to load the contract into the code editor. You can modify the code in the editor and reload the original contract code at any time, if needed. Click View to explore the Pact modules in a contract.
For example, if you select the Simple Payment contract, then click View for the payments modules, you'll see the functions and capabilities defined in the payments module.

Under Deployed Contracts, you san search for any contract that has been deployed to the network using the Module Explorer by name, by chain, or by navigating the pages using the arrow buttons.
After you select a deployed contract, you can click View to see details about what's defined in the contract, including implemented interfaces, functions, capabilities, and pact included in the contract. You can click Open to see the full contract code in the code editor.
You can also call individual functions from within the Module Explorer. You'll learn more about calling functions in Hello World.
Next steps
In this section, you set up your development environment with a local development blockchain network, Pact, and Chainweaver. You also explored the Chainweaver development environment by viewing full contract logic in the code editor, running simple Pact commands in the interactive REPL, and navigating through the features and tools for writing and testing smart contracts.
Before moving on, you might want to use the code editor and Module Explorer to get a more detailed view of the modules defined in the example and deployed contracts.
WHen you're ready, the next section introduces Pact with a simple "Hello, World!" contract. For the next steps, you'll:
-
Define a module for the
hello-worldcontract. -
Define an owner for the module using a keyset.
-
Define a function in the module.
-
Execute the module using the interactive Pact REPL interpreter.






